HOW TO DO BUSINESS IN SPACE?
The democratization of space is a growing phenomenon, involving the introduction of new actors and business opportunities. Just as the Internet was once the breeding ground for hundreds of startups, today space is the ecosystem providing a background for countless enterprising ideas.
Large companies and startups are using space in order to do business on Earth as it enables them to offer new services or generate key data for processing and commercialization purposes.

WHAT IS NEW SPACE?
The launch of Sputnik 1 marked the first victory in the conquest of space, and for over half a century increasingly larger and more expensive satellites designed to last for 40 years were launched. However, space was reserved for major corporations and space agencies.
Today the scenario has changed: a new wave is being carried out by small, fast and inexpensive systems that is enabling companies that need space to reach their objectives and expand their services to gain a foothold in this area. Hundreds of startups benefit from the savings involved in new small satellite constellations.
This small satellite revolution requires a new spatial ecosystem suitable for its constellations: a brand new productive environment that includes stations, satellite control and monitoring software, specialized subsystems, solar panels, batteries and rockets, etc.
Now more than ever, space is seen as a commercial enterprise. Large, medium-sized and startup businesses are all heading towards the final business frontier.

A FAST AND FLEXIBLE APPROACH
Before the emergence of New Space, the potential was not exploited due to economic and time constraints. The business opportunities arising from this ‘New Space’ stem from a model based on three key concepts:
FLEXIBLE
METHODOLOGIES
SHORT
DEVELOPMENT
LOWER
PRICES
BUSINESS OPPORTUNITIES IN SPACE
Space remains the ultimate challenge for humankind, yet in the business world, New Space has already taken shape—unlocking vast potential for the future. Small satellites allow for the collection, transmission and assessment of all kinds of data. Here at Alén Space we have developed a method which caters fully for the goals set by each company and sector.
The launch of small satellite constellations offers a global service that can be accessed 24 hours a day. Furthermore, the nature of this system means that loss of one satellite would not be catastrophic, as the service would remain active thanks to the rest of the constellation.
Short development times can also guarantee replacement in less than a year if any problem occurs.
Space is the ideal environment for the ongoing appearance of new business opportunities for entrepreneurs who know that getting there first can make the difference between success and failure. The future possibilities are endless, yet many small satellite applications have already been put into practice, creating added advantages and boosting profits for all kinds of companies and sectors.
Small Satellites, the Forefront of IOT
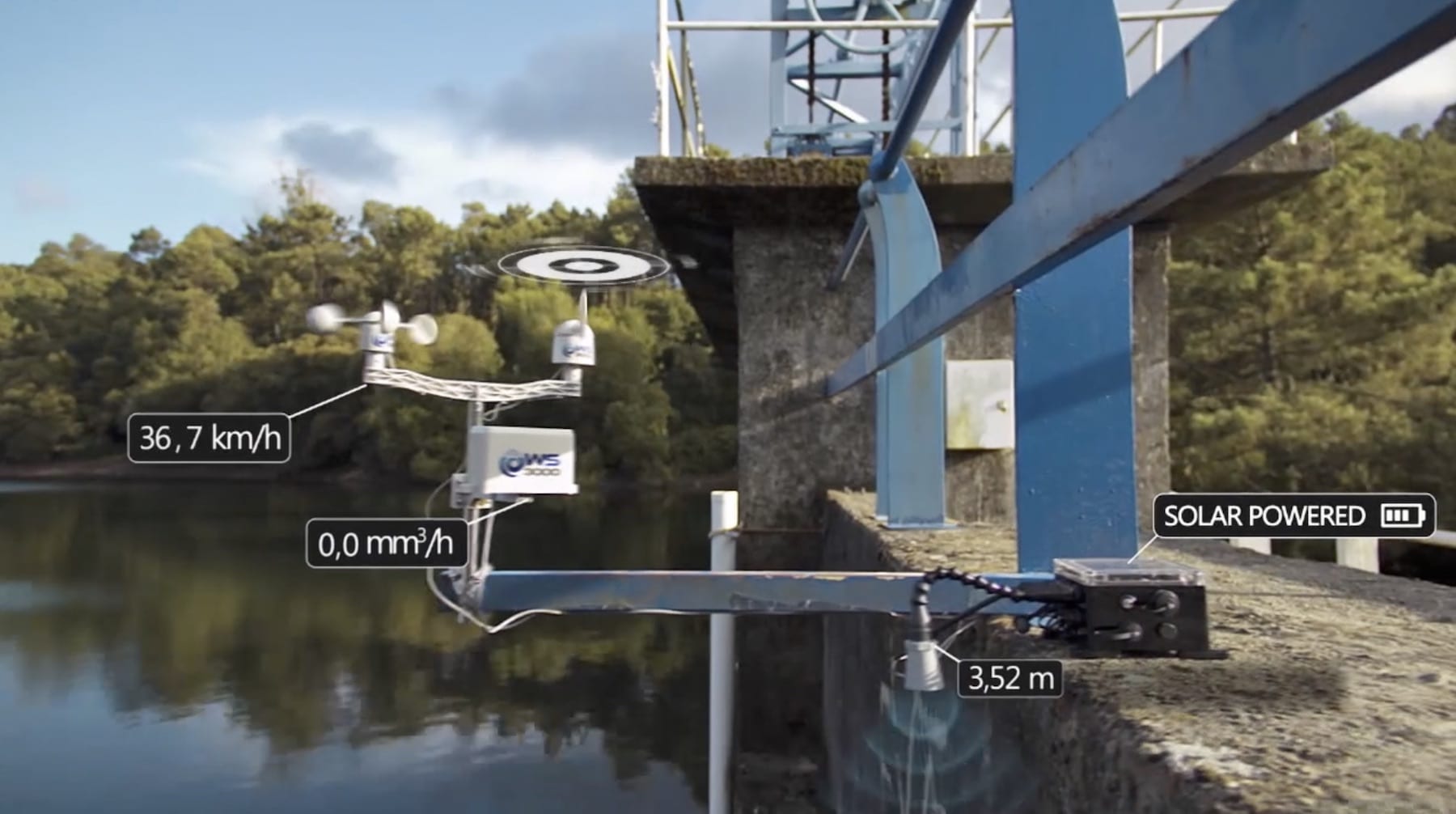
The Internet of Things (IoT) is changing multiple aspects of our daily lives, and CubeSats are playing a key role in this revolution.
They consist of constellations of small satellites in space and various sensors on Earth capable of generating vast amounts of data that are highly relevant for widely-differing areas, from air and maritime traffic monitoring to the optimisation of machinery and production facilities, or even autonomous transport operations.
Smart metering
Small satellites allow for machines and objects to communicate with one another. All that is needed is an identifier allowing for asset data and a connection enabling the satellites receive all types of information, including speed, temperature, energy consumption, etc. These smart measurements are essential to foresee future events, make informed decisions, and analyse records to detect problems.
Remote management
IoT technologies allow for the management and handling of all types of assets wherever they may be, based on the use of specific software. The satellites provide this communication with key assets located in remote areas and deliver the data companies require to carry out their activities and boost their efficiency levels.
ASSET TRACKING VIA SATELLITE
Small satellites allow for the precise tracking and geolocation of all types of assets in real time. Unlike land navigation systems, CubeSats can identify an object wherever it may be in the world – either in remote locations or at sea.
If it can’t be tracked, it can’t be controlled. Generally speaking, using a constellation of small satelites to track assets can be used for a wide range of needs. We can’t even begin to imagine the myriad applications this will offer in the future, but here are just a few of those that are here and now:

Aircraft tracking
Automatic Dependent Surveillance – Broadcast (ADS-B) allows for precise location of aircraft without the need for land radar signals. Aircraft transmit their GPS position, although occasionally the land reception of these messages is not possible, especially when the aircraft are flying mid ocean. A small satellite constellation can act as an intermediary, transmitting these messages and guaranteeing the tracking of passengers and freight.

Ship tracking
Communication between small satellites and ships allows for the real time tracking of their exact position in order to control the location and status of cargo. Ship tracking improves security and can also be used to manage routes and rescue operations, as well as avoiding collisions. This solution can also contribute to prevent piracy, detect illegal fishing or to carry out other environmental surveillance activities.

Fleet management
Fleet management systems are a practical way of tracking goods and passenger carriers. They are also useful for companies whose activities require the use of several vehicles or for Public Administration fleets. The data collected by small satellites allows for the precise tracking of each vehicle, as well as helping to take decisions aimed at boosting fleet productivity.

SIGINT (Signals Intelligence)
Small satellites can also detect the signals generated by third parties.
These small satellites can tune into certain frequency bands, identify broadcasts from Earth and space and analyse the electromagnetic spectrum of these frequency bands. They can be used to record unauthorised broadcasts, detect interferences and locate their origin. Even encrypted broadcasts can be geolocated, providing details of their modulation type and the areas they may be related to.
Consequently, in the event of a natural disaster, the small satellites will have prior information about impact levels and the most affected areas, thereby facilitating more effective rescue and relief work.